Targeting and Personalization
Targeting and personalization are the processes of delivering personalized content to one or more users. For example, if you are running a sports Web site, you may want to deliver tennis-related information only to tennis players, or to users who are interested in tennis. You may want to deliver announcements about upcoming tennis tournaments, or advertisements and promotions for tennis products.
You can use Commerce Server 2000 to perform two types of targeting:
- Expression-based targeting. Also known as explicit targeting. This is used when you know the profile properties of the users to whom you are delivering content, or you know the context, and you know what content is to be delivered. You use the Campaigns modules in Commerce Server Business Desk to specify this information and deliver the content to the user.
- Prediction. Also known as implicit targeting. This is used when you do not know all the necessary profile properties to target the user, or you do not have specific content to deliver. You use the Commerce Server Predictor resource to extrapolate this information from existing user data so that you can deliver content of interest to each user. For conceptual information about prediction, see Prediction and Data Mining.
Both expression-based targeting and prediction improve your ability to deliver content that may be of interest to the users who receive it. Users are more likely to return to your site when they can expect to receive a personalized experience.
Using Targeting Methods in Web Site Management
Expression-based Targeting
Expression Builder
Processing Expressions
Using Targeting Methods in Web Site Management
You can target content to any business-related item that has a profile. For example, you can target content to guest users, registered users, companies, or contexts. For conceptual information about profiles, see Profiles.
You use Business Desk to target content to business-related items. For example, you can do the following:
- Create a direct mail campaign that delivers personalized messages to users.
- Deliver content such as advertisements to users based on certain user profile properties. For example, you might display advertisements for bicycles to users who have their Favorite Sport property set to "Biking."
- Identify groups of Web pages, and then target content to be displayed only on those pages, or only if the user accesses those pages.
- Display content on a page based on the properties of other content on the page. For example, if your Web site provides news, you can assign profiles to the content specifying whether Weather_Type property is "Hot" or "Cold." If Weather_Type = Hot, you can display an advertisement for air conditioners.
- Apply discounts to certain products in your catalog, based on characteristics of the product itself, or based on the user profile.
- Choose when to display a discount and when the discount is to be applied to the order. For example, you can apply the discount when users put the item in their basket or when they check out.
Expression-based Targeting
Expression-based targeting is the process of creating expressions that define the users or context you want to target and the content you want to deliver. An expression is a condition that is evaluated against profiles to determine whether to deliver content, or perform another action. For example, an expression might be user.totalvisit > 100. If this expression evaluates to "True," then a specific piece of content is displayed to the user.
You use the Campaigns modules in Business Desk to create expressions, and then combine the expressions with the action you want to perform after the expression is evaluated. You can create two types of expressions:
- Target expressions. Identify where, when, and to whom content should be displayed. For example, you can target content to users who have specific profile properties. You can also target content to specific sections of a Web site, called page groups. For example, you can create a target expression that will display certain ads only on sports pages.
- Catalog expressions. Specify the products in a catalog that a discount can be applied to. For example, a catalog expression might be Product.price = 20.00. If this expression is "True," for a particular product, then a discount of 10 percent is applied to the price of that product when users add it to their shopping baskets.
After you have created target expressions, you can combine them to form a target group. A target group is a collection of expressions and actions. For example, you might create one expression to show a specific piece of content to users who have visited the site 10 times, and another expression to show content to users who have purchased a soccer shirt. You can combine the two expressions in a target group with AND or OR statements. For example:
If the user has visited the site 10 times AND the user has purchased a soccer shirt,
Display an advertisement for a soccer product.
In a target group you combine expressions by specifying the action to be taken when each expression evaluates to "True." Each action has two multipliers: a multiplier to apply if the expression is "True," and a multiplier to apply if the expression is "False." When the multiplier is applied, the expression is given a score, which affects whether the content is eligible for delivery. You can specify the following actions:
- Target. If the expression evaluates to "True," the score is increased, as is the probability the content will be shown. If the expression evaluates to "False," the score is not changed. In both scenarios, the content is eligible for delivery.
- Require. If the expression evaluates to "True," the content is eligible for delivery; if it is "False," the content is not eligible for delivery.
- Exclude. If the expression evaluates to "True," the content is not eligible for delivery; if it is "False," the content is eligible for delivery.
- Sponsor. If the expression evaluates to "True," the content is eligible for delivery and no other content is eligible unless it too has an expression with action = Sponsor. (Sponsor has only one multiplier.) For example, if Microsoft were to sponsor an advertisement on a home page, only Microsoft advertisements would be displayed; however, if there are more advertisements from other companies sponsoring the home page, those advertisements would also be eligible for display.
A site developer can change the values of the multipliers provided with Commerce Server. You may want to do this to give expressions with one action type a higher priority than expressions with a different action type.
Expression Builder
The Commerce Server feature that enables business managers to create, edit, and view expressions is called the Expression Builder. The Expression Builder provides the user interface for building expressions. It accesses the appropriate properties for building an expression, and it names and stores the expression in the Commerce Server databases.
The Expression Builder is designed so that site developers can easily embed its functionality and user interface in other Business Desk modules. In addition, it can be invoked by any Web application that uses and manipulates expressions, enabling you to integrate it with other processes. For example, if you have an existing content management process, you can incorporate Expression Builder functionality, and then target content to users.
To create applications that use the Expression Builder, you do the following:
- Define profiles. You specify which profiles the expression should use, and the Expression Builder loads those profile definitions for constructing the expression. You can also specify a profile properties filter to limit the properties in the profile that will be available to an Expression Builder user.
- Save expressions. You can specify the expression/profile store to use, and the Expression Builder loads and saves expressions in that database.
- Display messages to users. You can customize the messages that are displayed in the Expression Builder user interface (UI). For example, the default title message is "Create an expression," but for your implementation, you might change it to "Create an Ad Targeting Expression."
The Expression Builder uses DHTML for its UI, so the stylesheets of the application will apply to the Expression Builder UI, giving your application a consistent look and feel.
Processing Expressions
Commerce Server performs several steps to specify the piece of content that is to be shown to a user. The following components are used in the process:
- ExpressionEval. This Component Object Model (COM) object takes the expression and user data as input, and then processes the expression to determine whether it evaluates to "True" or "False."
- Content Selection Framework (CSF). This platform-level framework includes a set of components and pipelines (the Content Selection Pipeline and the Event Processing Pipeline) that determines the action to be performed as a result of the expression.
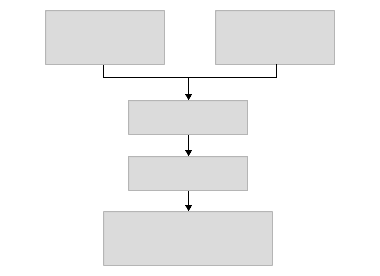
The following figure illustrates how target expressions, catalog expressions, user data and context data are input into the Expression Evaluator, which results in True, False, or undefined results. The result is input to the CSF, which then determines the action to perform.
True, False, or undefined result
Content Selection Framework
Determines the action on this result
See Also
Prediction and Data Mining
Campaigns: Ads, Discounts, and Direct Mail
Copyright © 1996–2000 Microsoft Corporation.
All rights reserved.